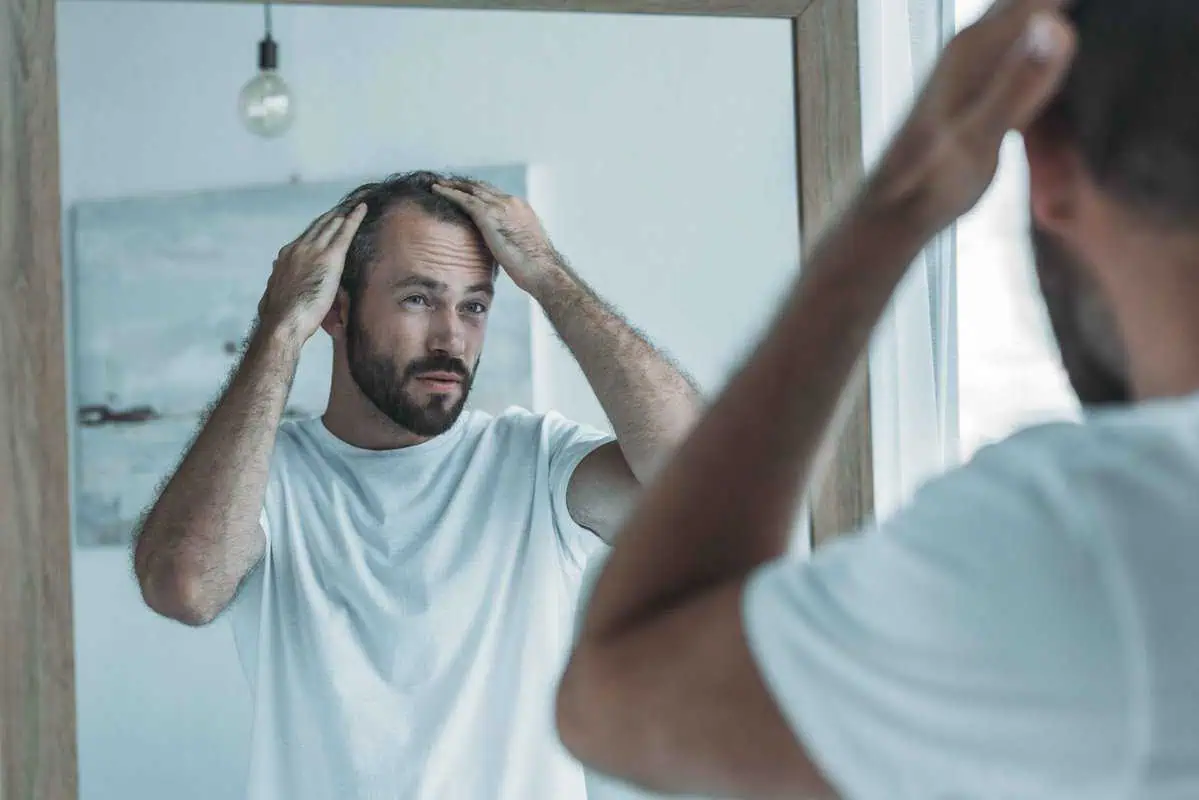
Hair loss affects millions across all genders, ages, and ethnicities. While occasional shedding is natural, notable thinning or balding can cause distress. Both men and women seek solutions to this challenge. Rejuve Wellness and Aesthetics in Woodlands and Montgomery, TX, focuses on effective hair loss treatments. This article explores the primary causes of hair loss in both genders, highlighting genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. As we explore these causes, readers will understand this common concern better.
Common Causes of Hair Loss in Both Men and Women
Hair loss isn’t just an aesthetic concern—it can often indicate underlying health issues or bodily shifts. Various factors can trigger those receding hairlines or thinning patches for both men and women. Let’s dive straight into the most prevalent causes.
1. Genetic Factors:
- Male Pattern Baldness: Most men notice hair thinning by age 35, with about 85% experiencing significant thinning by age 50. Genetics plays a vital role here.
- Female Pattern Hair Loss: It’s a misconception that only men suffer from genetic hair loss. Women also face this challenge, although the pattern of loss often differs.
2. Hormonal Changes and Imbalances:
- Men and Androgens: Elevated levels of male hormones can accelerate hair loss.
- Women and Menopause: The hormonal shifts during menopause can lead to hair thinning.
- PCOS: Polycystic ovary syndrome, a common hormonal disorder among women, often presents hair thinning as a symptom.
3. Stress and Traumatic Events: Stress disrupts the hair growth cycle, resulting in temporary hair loss. Events like childbirth can temporarily increase hair shedding in women.
4. Medications and Supplements: Certain drugs and excessive vitamin A intake can cause hair loss.
5. Illnesses and Medical Conditions:
- Alopecia Areata: This condition causes hair loss.
- Thyroid Disorders: Both overactive and underactive thyroids can thin hair.
- Diseases like lupus and anemia also play culprits in hair loss scenarios.
6. Nutritional Deficiencies: Hair thrives on essential nutrients like iron, zinc, and biotin. Their deficiency can lead to hair loss. A protein-deficient diet can also impact hair health.
7. Hair Care and Styling Practices: Using high-heat tools or chemical treatments regularly weakens hair strands. Tight hairstyles can cause traction alopecia, leading to hair breakage and loss.
8. Environmental Factors: Pollution damages hair, making it more prone to breakage. Extended exposure to the sun’s UV rays can weaken hair structure and lead to thinning.
Understanding the causes of hair loss helps manage the problem. Awareness is vital for prevention and treatment.
Hormonal Changes and Imbalances: Their Role in Hair Loss
Hormones act as our body’s chemical messengers, influencing many physiological processes. But did you know they also play a pivotal role in the health of our hair? Changes or imbalances in hormone levels can significantly impact hair growth and loss. Let’s explore the different hormonal factors that can affect our luscious locks.
- Androgens and Men: Androgens, primarily male hormones, can contribute to hair thinning. Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a crucial player, causing hair follicles to shrink and, thus, reducing their lifespan. An increase in DHT levels can accelerate male pattern baldness, making it more pronounced in some men than others.
- Menopause and Women: Menopause brings about a decline in estrogen and progesterone—two hormones that help hair grow and stay on the head for longer. Hair growth slows as these hormone levels drop, and shedding can increase. It often results in overall hair thinning rather than distinct bald spots.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): People with PCOS have thin hair on their scalps and excessive hair growth elsewhere.
- Pregnancy and Post-Partum Changes: Pregnancy sees a surge in estrogen levels, leading many women to experience thicker hair. – However, post-partum, these levels drop, potentially resulting in increased hair shedding, often referred to as “post-partum hair loss.”
- Thyroid Imbalances: The thyroid gland produces hormones essential for metabolism and growth. Overactive (hyperthyroidism) or underactive (hypothyroidism) thyroids can disrupt hair growth.
- Stress and Cortisol: Cortisol, often termed the “stress hormone,” increases during prolonged periods of stress. Elevated cortisol levels can disrupt the hair growth cycle, potentially leading to hair loss.
Understanding how hormonal shifts impact our hair offers insights into potential preventative measures and treatments. If you suspect a hormonal imbalance is behind your hair loss, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough assessment and guidance.
Illnesses and Medical Conditions
Hair loss can be attributed to various diseases and medical conditions, including genetics and hormones. It’s not just about vanity; your hair’s condition can often act as a mirror, reflecting underlying health issues. Let’s delve into the medical reasons behind those thinning strands.
- Alopecia Areata: This autoimmune disorder’s immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles. This attack leads to sudden hair loss, often in small, round patches on the scalp.
- Thyroid Disorders: Both overactive (hyperthyroidism) and underactive (hypothyroidism) thyroid glands can lead to hair thinning or loss. Since the thyroid gland regulates metabolism, an imbalance affects the hair growth cycle.
- Lupus: Lupus is another autoimmune disease, and its manifestations are diverse. Many lupus patients report hair loss in clumps or evenly spread, especially during flare-ups.
- Iron-Deficiency Anemia: Iron is essential for hair growth. A deficiency often results from poor diet, heavy menstrual periods, or ulcers. People with iron-deficiency anemia often experience hair loss, among other symptoms.
- Ringworm of the Scalp: This is a fungal infection known as tinea capitis. It’s not a worm! It creates scaly, circular patches on the scalp and can lead to broken hair and bald spots.
- Scalp Psoriasis: This chronic skin condition results in a buildup of skin cells, forming red, itchy patches on the scalp. While it doesn’t cause hair loss directly, scratching or harsh treatments can lead to temporary hair shedding.
- Lichen Planus: This is another inflammatory skin condition where patients might notice shiny, flat bumps on the skin or in the mouth. When it affects the scalp, it can lead to hair loss.
- Secondary Syphilis: One of the lesser-known symptoms of syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection, is hair loss. It typically presents uneven hair loss, creating a “moth-eaten” appearance.
Consult a Professional
It’s essential to note that you should consult a medical aesthetician if you’re experiencing sudden or unexplained hair loss. They can provide a proper diagnosis and guide you on the next best steps for treatment or management.
Takeaway
Understanding hair loss is the first step toward addressing it. If you’re ready to take action, Rejuve Wellness and Aesthetics in Woodlands and Montgomery, TX, is here to help. Dive deeper into tailored solutions for your hair concerns. Contact us today or book an appointment to begin your journey to healthier hair.